Revolutionizing Hyperacute Stroke Care: An Approach
for Early Detection using Artificial Intelligence
Executive Summary
- 🌟 Vision: Redefine the future of healthcare by leveraging machine learning to save lives, limbs, and uphold human dignity in the face of the global stroke epidemic.
- 🚀 Mission: Empower Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) with cutting-edge stroke care through the free deployment of the revolutionary NeuroICH AI Model.
- 🤝 The Driving Force: The Institute of Health Innovation and Education, a registered non-profit organization in the Texas, United States
- 🔍 Partnership: In collaboration with our partner, NeuroCareAI, we present a groundbreaking initiative. The NeuroICH AI Model, developed by NeuroCareAI, is poised to revolutionize stroke care, and we are committed to making this innovation accessible at zero cost to LMICs.
- 📈 Current Progress: We have initiated the working from Pakistan. Application and System Integration:
- Completed in 02 hospitals
- Working under progress in 09 hospitals
- Planned to be initiated soon in 04 hospitals
- ⏰ Future Plans: We are ready to integrate our application in more hospitals as soon as funds are received.
- 📍 Rollout Strategy: Commencing in Pakistan, Bangladesh, and India, our mission is to extend this life-saving technology for free to all Low- and Middle-Income Countries, creating a ripple effect of positive change.
Why Fund?
Join us in revolutionizing healthcare’s future! Your support fuels saving lives and limbs against the staggering impact of strokes worldwide through an environment friendly technology.
- 🌍 Projected Impact:
- 🦿 Save Lives and Limbs: Over five years in each country, envision the ripple effect: 500,000 lives saved, 3.95 million Disability-adjusted life years (DALY) decreased, and an astonishing $3.2 billion reduction in healthcare costs.
- 🌱 Environmental impact: ~300 million tons decrease in plastic waste, $1.3 trillion reduction in waste management costs.
Sponsorship Packages
Silver
- Small size imaging center integration and service
- [10,000 scans per year]
We will provide:
- Edge Device
- Integration support
- One year of Cloud expenses
$500/month
Gold
- Medium Size imaging center integration and service
- [25,000 scans per year]
We will provide:
- Edge Device
- Integration support
- One year of Cloud expenses
$750/month
Platinum
- Large Size imaging center integration and service
- [50,000 scans per year]
We will provide:
- Edge Device
- Integration support
- One year of Cloud expenses
$1000/month
Large-Scale Sponsorship
- We possess the capability to facilitate widespread deployment of this application, extending its reach to encompass entire countries.
Sponsorship starting from
$2 million, ensuring sustainable support and development for up to 5 years.
Goal
To utilize artificial intelligence and digital care coordination for enhancing acute stroke care by reducing latency, saving lives and limbs
Gap Analysis and Proposed Solution
Stroke, the second leading cause of death globally, is responsible for approximately 11% of total deaths and is a major contributor to long-term disability (WHO, 2023). In the United States, a stroke occurs every 40 seconds, affecting over 795,000 individuals annually, with around 610,000 of these being new or first-time strokes. More than half of stroke survivors aged 65 and above face a significant decline in their mobility, underscoring the profound impact this condition has on their daily functioning (Tsao CW et al., 2023). Receiving prompt stroke care is critical because with each moment that passes without treatment, brain cells are lost. Studies have repeatedly shown that seeking early treatment greatly improves the chances of recovery and hence gain in disability free life (Benjamin EJ et al., 2018) (Figure 1).
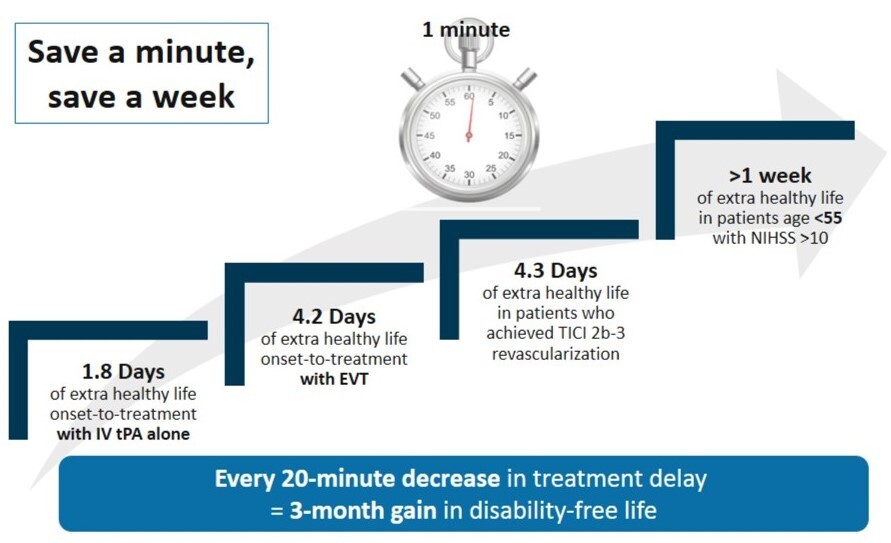
Figure 1: Impact of saving time in the provision of treatment to stroke patients (Meretoja A et al., 2017)
According to the findings of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2017, stroke ranked as the second highest contributor to DALY in middle-income nations and the third highest in low-income nations. This study revealed that approximately 57 million individuals worldwide were stroke survivors in 2017, with roughly 80% of these individuals residing in low- and middle-income countries (Roth GA et al., 2018). Moreover, a meta-analysis conducted in 2018 established that the incidence of strokes in low-income countries is roughly twice as high as in high-income countries, while the mortality rates associated with strokes are also elevated in low- and middle-income countries (Feigin VL et al., 2018).
The cost of stroke care is on the rise, with annual expenditures showing a significant increase. At present, stroke is responsible for approximately $36.5 billion in healthcare expenditures in the United States each year. However, projections indicate that the total medical costs related to stroke are expected to more than double, reaching a staggering $94.3 billion. A considerable portion of these costs can be attributed to patients who require specialized care, such as those in nursing homes, skilled nursing facilities, and other long-term healthcare facilities (Tsao CW et al., 2023). Consequently, providing early access to treatment for stroke patients can lead to substantial cost savings. By ensuring prompt and efficient care, we have the potential to mitigate the financial burden associated with stroke and improve patient outcomes.
We propose to implement the digital technology “NeuroICH AI Model” in clinical settings to bring about a revolutionary change in hyperacute care, particularly in stroke treatment. Our partner company, NeuroCareAI has developed this model and is willing to make it available at no additional cost for free to LMICs. By using our NeuroICH AI Model we can significantly reduce the time it takes to administer care, leading to better patient outcomes and the potential to save more lives. Our cutting-edge solution has the potential to disrupt the conventional approach to hyperacute care.
What is NeuroICH?
NeuroICH is an advanced AI model that can provide brain scan images at par with the gold standard CT scan machines used by the radiologists in hospitals. It is designed to accurately identify bleeding in brain, making it particularly useful in diagnosing this critical conditions. With this cutting-edge technology, healthcare providers can obtain precise brain scans to facilitate prompt diagnoses and targeted treatments, improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
We have trained our AI model on open datasets and were able to achieve overall accuracy of 98% for detection of ICH with no accuracy less than 97% for individual ICH types. The sensitivity and specificity of the NeuroICH model is 97.5% and 97.4% respectively.
Project Aim
The aim of the project is to implement NeuroICH AI Model in the hospital setting in order to create a comprehensive digital care coordination platform that facilitates contextual communication between relevant stakeholders involved in stroke care. This platform will enhance collaboration and information exchange among healthcare providers, radiologists, neurologists, emergency response teams, and other involved parties, ultimately improving the coordination and quality of care for stroke patients.
Project Implementation
The project implementation plan will commence by establishing collaborations with hospitals and clinicians in LMICs. These collaborations are crucial for ensuring the successful execution of the project. Once the partnerships are in place, the next step will involve deploying a prototype of the NeuroICH model in a real-world clinical setting. This prototype will be thoroughly tested, validated, and verified to assess its functionality, usability, and effectiveness.
During the testing, validation, and verification phase, comprehensive assessments and analyses will be conducted to ensure the proper working of the NeuroICH model. Any identified issues or discrepancies will be addressed, and necessary adjustments will be made to enhance the utility of model in the hospital.
Following the successful completion of testing, validation, and verification, the final delivery of the NeuroICH model will take place. This will involve the installation of edge devices at the participating hospitals. These devices have the capacity to securely store large amounts of patient data generated by the NeuroICH model. The installation process will be carried out in collaboration with the hospitals’ IT teams to ensure seamless integration with their existing infrastructure.
Prototype Image
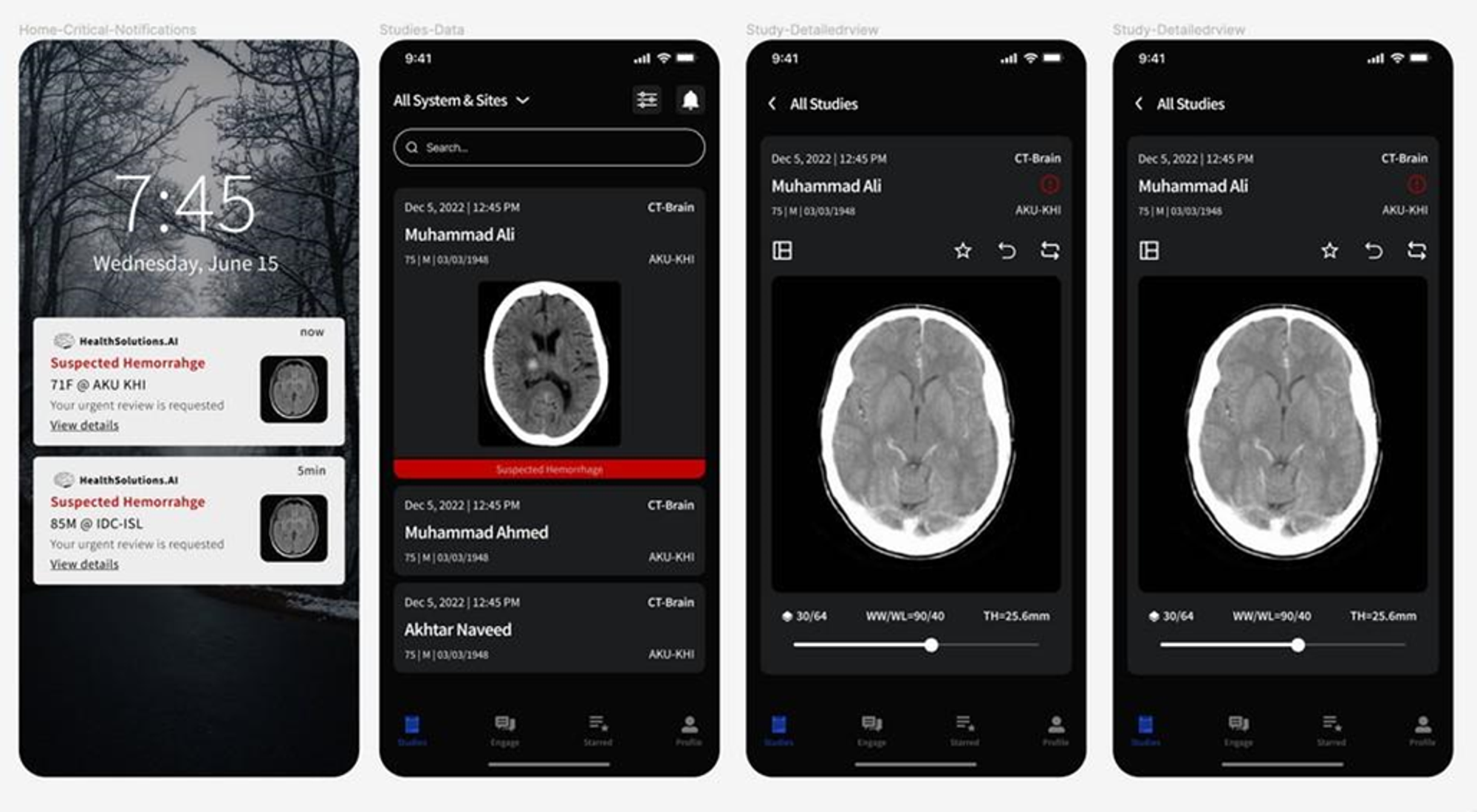
Figure 2: Prototype image of the NeuroICH model showing the generation of notification alert and the brain scan
Project Sustainability
Current Progress
We have already started the integration of the application in various hospitals and medical centers of Pakistan.
Integration Completed
| SNo. | Site | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Holy Family Hospital | Hospital |
| 2. | Sarwar Foundation Hospital | Hospital |
Integration Initiated and Currently in Progress
| SNo. | Site | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rai Ali Nawaz Hospital | Hospital |
| 2. | Al-Madina Diagnostics | Radiology Center |
| 3. | Abid Imaging Center | Radiology Center |
| 4. | Bashir Diagnostic Imaging Center | Radiology Center |
| 5. | Sandho Diagnostic Center | Hospital |
| 6. | Modern Diagnostic Center | Radiology Center |
| 7. | Pak CT Scan Center | Radiology Center |
| 8. | Mian Diagnostics | Radiology Center |
| 9. | Ittefaq 3D CT Scan | Radiology Center |
Integration Process to be Initiated Soon
| SNo. | Site | Type | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Shifa Hospital | Private Hospital | Demo Given – Approved by HOD Neurology |
| 2. | Ghurki Hospital | Trust Hospital | Demo Given – Awaiting Response |
| 3. | Services Hospital | Teaching Hospital | Demo Given to HOD – Awaiting Administration’s Approval |
| 4. | Gulab Devi Hospital | Teaching Hospital | Demo Given – Awaiting HOD’s Response |
Social Impact of the Project
- Early Detection and Diagnosis: One of the primary impacts of the NeuroICH is its ability to detect intracranial hemorrhages at an early stage. By accurately identifying even small hemorrhages, the model enables healthcare professionals to initiate timely interventions, such as surgical procedures or medical treatments, to mitigate the potential damage caused by the bleeding. Early detection and diagnosis can lead to better patient outcomes, reduced complications, and improved survival rates.
- Improved Patient Care and Outcomes: The NeuroICH empowers healthcare professionals with a powerful tool to aid in the diagnosis and management of brain hemorrhages. By providing timely and accurate insights, the model enables healthcare teams to make informed decisions regarding treatment strategies, appropriate interventions, and patient care plans. This, in turn, can lead to more personalized and effective treatment, optimized resource utilization, and ultimately improved patient outcomes.
- Decrease Cost: Providing early treatment access to stroke patients has the potential to yield substantial annual cost savings, estimated to be up to $800 million in the United States. A significant portion of these savings can be attributed to the expenses associated with specialized care and long-term healthcare facilities provided to stroke patients. By enabling timely intervention and treatment, the need for prolonged hospital stays, extensive rehabilitation programs, and ongoing care in nursing homes or other long-term healthcare settings can be reduced. This not only alleviates the financial burden on the healthcare system but also improves the overall quality of life for stroke survivors by facilitating their recovery and reintegration into their communities. Such cost savings underscore the importance of early detection and intervention in stroke care, emphasizing the need for accessible and efficient healthcare services to optimize patient outcomes while minimizing healthcare expenditure.

Figure 3: Impact statistics of early treatment to stroke patients
Environmental Impact of the Project
- Environmental Sustainability: By eliminating the need for radiology films in health care, the project significantly reduces environmental pollution associated with film production and disposal. This eco-conscious approach aligns with global efforts to reduce healthcare’s environmental footprint, contributing to a healthier planet.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By eliminating radiology films, the project reduces the carbon footprint associated with film production, transportation, and disposal. This reduction in healthcare-related environmental impact aligns with global efforts to combat climate change.
- Improved Health: Embracing eco-friendly solutions in healthcare holds immense promise for improving public health on a global scale. By reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and transitioning to cleaner, renewable energy sources, we can significantly reduce air pollution, resulting in fewer cases of respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and even premature deaths.
- Decrease in Plastic Waste: The project anticipates a noteworthy environmental achievement, aiming to reduce plastic waste by approximately 300 million tons (UN Foundation Report 2023). This ambitious goal signifies a significant stride in curbing the detrimental impact of plastic pollution on our ecosystems.
- Reduction in Waste Management Costs: A key economic advantage of the project lies in its potential to bring about a substantial reduction in waste management costs, estimated at approximately $1.3 trillion (World Wildlife Fund, 2023). This financial efficiency not only promotes sustainable practices but also addresses the economic burden associated with waste management on a global scale.

Figure 4: Impact of NeuroICH on environment preservation
References
Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2018 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67-e492.
Feigin VL, Nguyen G, Cercy K, et al. Global, regional, and country-specific lifetime risks of stroke, 1990 and 2016. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(25):2429-37.
Meretoja, A., Keshtkaran, M., Tatlisumak, T., Donnan, G. A., & Churilov, L. (2017). Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke: save a minute—save a week. Neurology, 88(22), 2123-2127.
New York Times report. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/03/01/magazine/evt-stroke-treatment.html (Accessed on October 8, 2023).
Roth, G. A., Abate, D., Abate, K. H., Abay, S. M., Abbafati, C., Abbasi, N., … & Borschmann, R. (2018). Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet, 392(10159), 1736-1788.
Tai, W. A., Conley, J., & Kalanithi, L. (2014). Cost-saving innovations for acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. Neurology: Clinical Practice, 4(5), 427-434.
Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Beaton AZ, Bittencourt MS, Boehme AK, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2023 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2023;147:e93–e621.
United Nations Foundation Report. https://unfoundation.org/blog/post/protect-our-planet-from-plastic-pollution-5-things-to-know/ (Accessed on October 8, 2023).
University of Melbourne report. https://research.unimelb.edu.au/strengths/updates/impact/reaching-stroke-patients-in-time-to-give-life-saving-treatment (Accessed on October 8, 2023).
World Health Organization (WHO), 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death Accessed on May 29, 2023.
World Wildlife Funds Report. https://wwf.panda.org/wwf_news/?3507866/These-costs-for-plastic-produced-in-2040-will-rise-to-US71-trillion-unless-urgent-action-is-taken#:~:text=1.,plastic waste generated every year. (Accessed on October 8, 2023).
The need for modern care and education system has never been greater. Sign up for our newsletter.